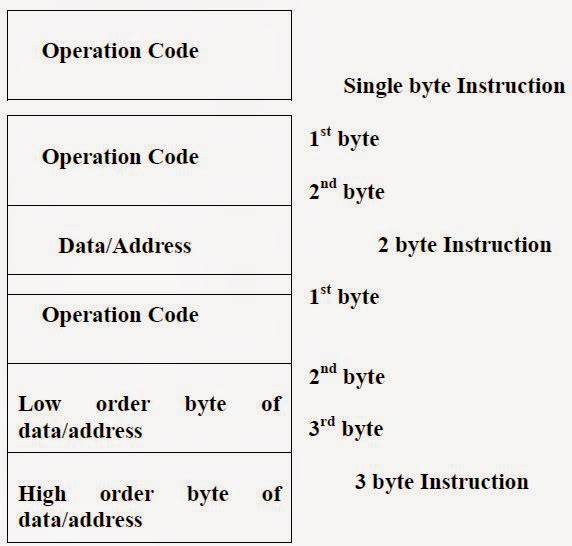
Encoding of Information
In computers, encoding is the process of putting a sequence of characters (letters, numbers, punctuation, and certain symbols) into a specialized format for efficient transmission or storage. Decoding is the opposite process -- the conversion of an encoded format back into the original sequence of characters. Encoding and decoding are used in data communications, networking, and storage. The code used by most computers for text files is known as ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange). ASCII can depict uppercase and lowercase alphabetic characters, numerals, punctuation marks, and common symbols. Other commonly-used codes include Unicode, BinHex and Uuencode. In data communications, Manchester encoding is a special form of encoding in which the binary digits (bits) represent the transitions between high and low logic states. Operation Code (Opcode) It specifies the operation to be performed. The operation of the CPU is determined by the instructi...